上篇文章中介绍了单线程化线程池newSingleThreadExecutor,可控最大并发数线程池(newFixedThreadPool)与其最大的区别是可以通知执行多个线程,可以简单的将newSingleThreadExecutor理解为newFixedThreadPool(1)。例如运行一下两个程序:
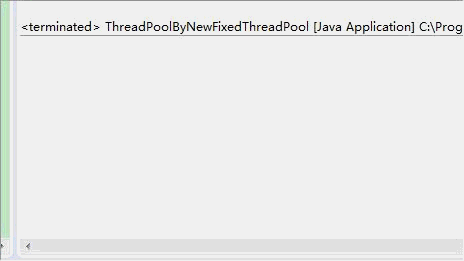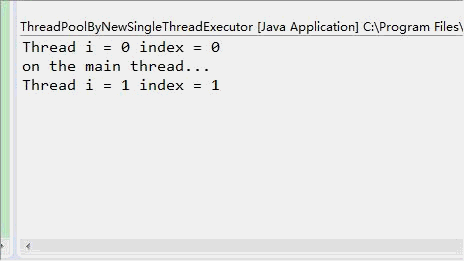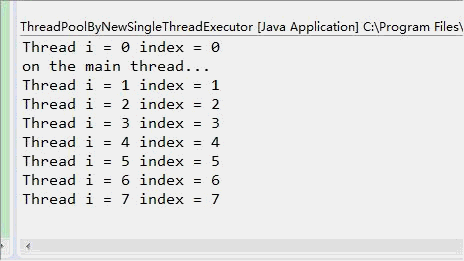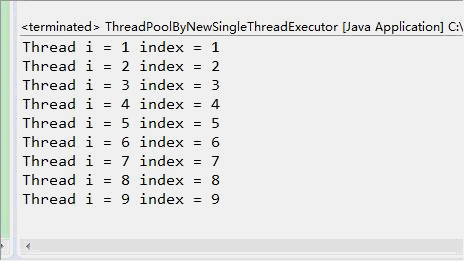
单线程化线程池(newSingleThreadExecutor)示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadPoolByNewSingleThreadExecutor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int index = i;
singleThreadExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Thread.currentThread().setName("Thread i = " + index);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " index = " + index);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("exception");
}
}
});
}
singleThreadExecutor.shutdown();
System.out.println("on the main thread...");
}
}
|
可控最大并发数线程池(newFixedThreadPool)示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadPoolByNewFixedThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int index = i;
newFixedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Thread.currentThread().setName("Thread i = " + index);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " index = " + index);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("exception");
}
}
});
}
newFixedThreadPool.shutdown();
System.out.println("on the main thread...");
}
}
|
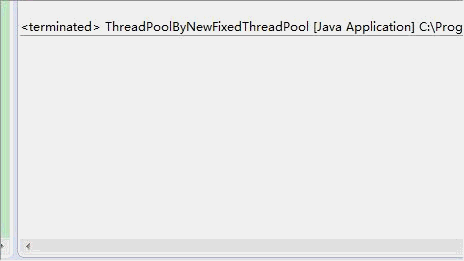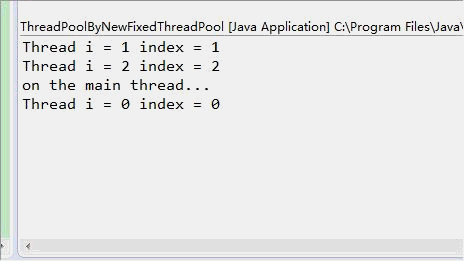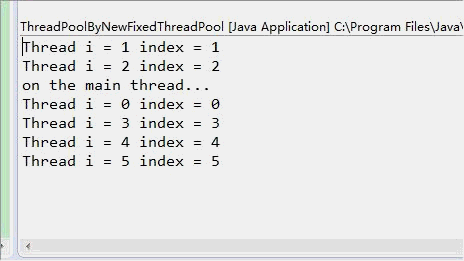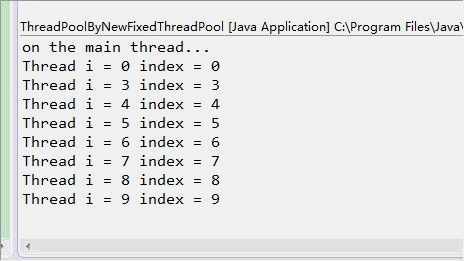
结果从显示上看虽然很相似,但是观察到的执行效果确实完全不一致的,newSingleThreadPool中,只有一个线程,每次输出一行后暂停0.5秒,newFixedThreadPool(3)中可以创建3个线程,一次输出3行后暂停0.5秒(当然是这三个线程都暂停0.5秒)。
动画对比如下所示: